Oregon Shade Credits
The Oregon Environmental Quality Commission approved a voluntary water quality trading program to reduce pollution and protect the quality of Oregon’s waterways.
As part of this program, municipalities and other industry can offset their water thermal pollution with the placement of new shade riparian plantings.
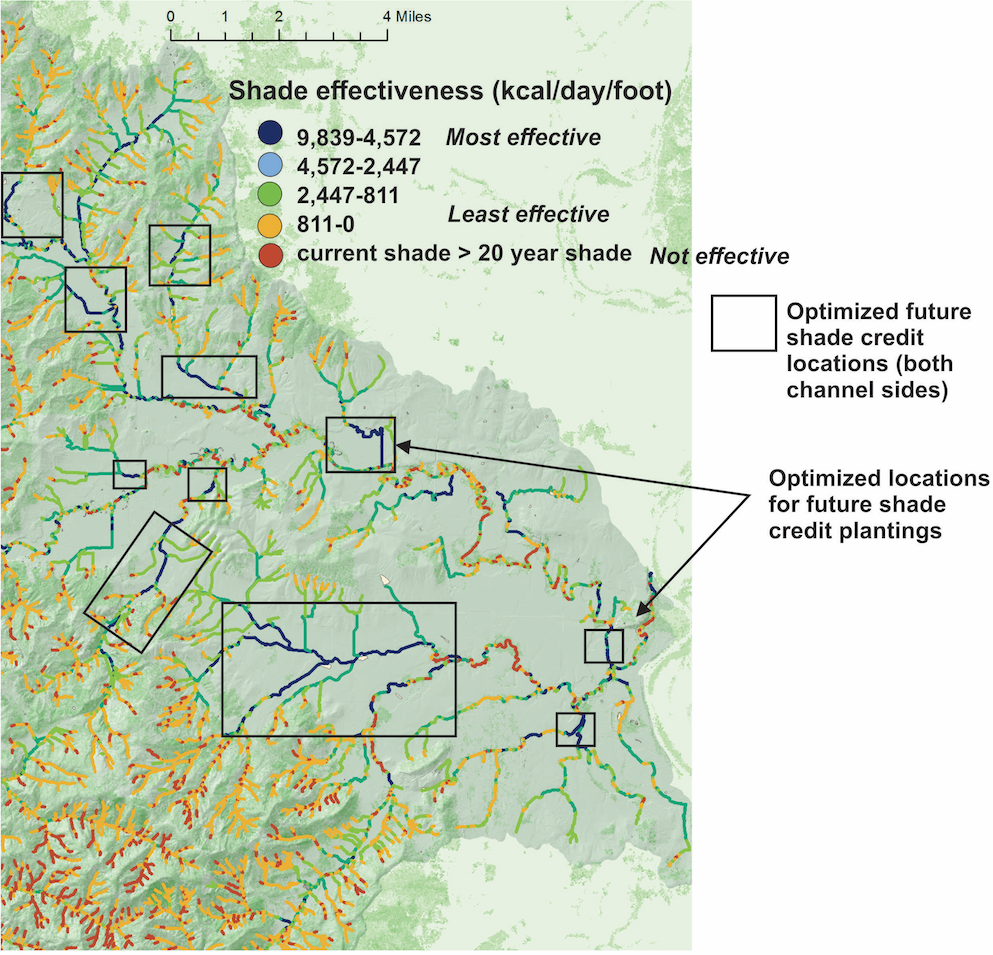
at the scale of entire watersheds, where are the best locations to place to shade to optimize their effectiveness?
TerrainWorks has developed a NetMap tool to evaluate new shade credit effectiveness across entire watersheds for prioritizing new project locations (optimization).
The tool mimics the ODEQ Heat Source - Shade-o-later model using an average riparian planting width of 50 feet and a vegetation density of 0.75. It calculates total daily solar radiation load for the hottest day of the year, August 10. The tool uses the estimated 20-year old vegetation. Thermal load reduction is converted to kilocalories.
The model evaluates plantings on both sides of the streams and only on one side of the stream (left or right).
You can create a watershed map that shows where the best locations are for increased shade according the Oregon’s Shade Credit Program
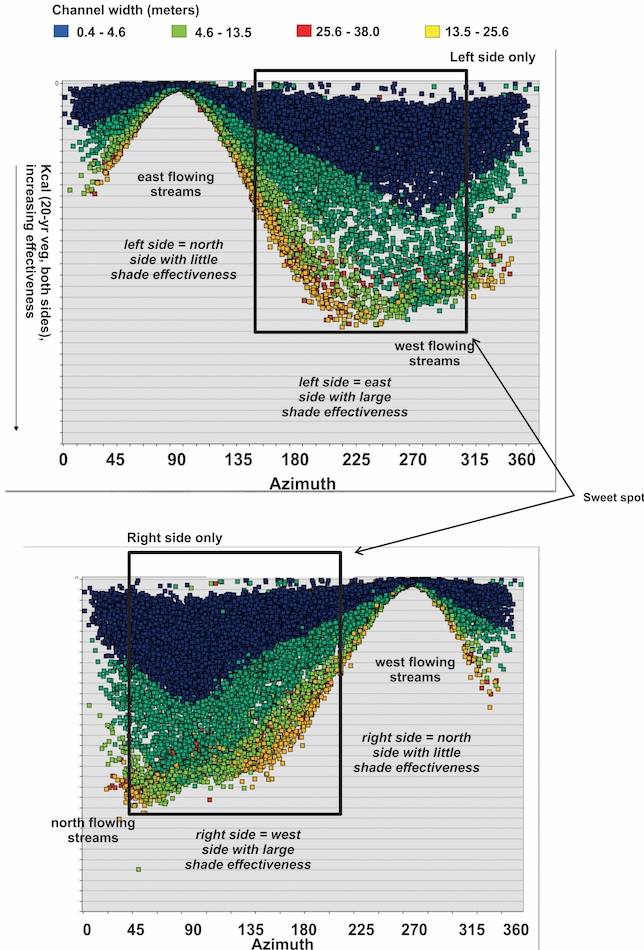
Calculate shade effectiveness on only a single channel side
(example - left side channel only, looking downstream)
Which side of the channel matters, particularly in east / west flowing streams.
This chart illustrates how stream azimuth and channel width matter in site selection